Emergency
care of moderate and severe thermal burns in adults
In
worldwide thermal burns are the leading cause of accidental injury and death. In
spite of the fact that the vast majority of injuries do not require
hospitalization, severe burns can lead to significant morbidity and death.
The
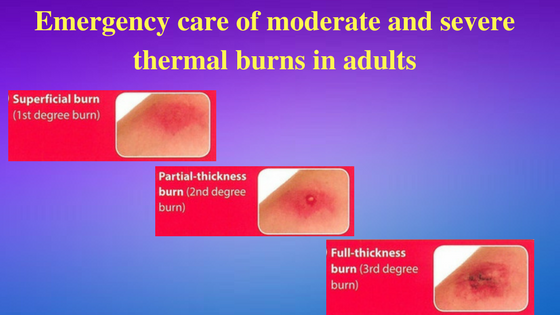
overall severity of the burn injury (minor, moderate, severe) can be determined
by a combination of the burn mechanism, burn depth, extent, and anatomic
location, which gives general guidance for the preferred disposition and care
of these patients. In this manner it is essential that clinicians properly
characterize the size and severity of their patients' burns. Reassessment of
thermal burn size and depth is important, especially early in the management of
patients with severe injuries, as the extent of injury often increases.
Initial Assessment
and Treatment:
Initial
treatment and assessment of severe burn cases is performed simultaneously with
trauma resuscitation. The main focus for initial management is to stabilizing
the airway, breathing, and circulation (ABC's).Evidence of respiratory distress,
smoke inhalation injury, monitoring cardiovascular status, looking for different
injuries, and monitoring the depth and
extent of burns are includes in the primary assessment.
Airway management:
Assessment:
Inhalation injury remains a leading or main cause of death in adult burn
victims, despite advances in ventilatory management. Depending upon the extent
of the burn, the risk of inhalation injury increases. While assessing the
airway, clinicians should immobilize the patient's cervical spine as
appropriate. It is critical to keep the airway and provide supplemental oxygen in
patients with major burns.
Diagnostic
tests: Although the initial results may be normal, studies to assess pulmonary
function should be obtained in patients at risk for inhalation injury. These
include an arterial blood gas (ABG) and a chest radiograph. These are
particularly useful early in a patient’s course.
Treatments:
Supplemental oxygen and airway protection are most important of treatment for
inhalation injury. The severe burn patients often require tracheal intubation.
Although fluid resuscitation is critically essential in managing patients with
significant burns, fluid status should be closely monitored in order to avoid
overhydration.



Comments
Post a Comment